Products
Characteristics of industrial dust
Origin:Hefan Hit: Time:2020-02-28
Industrial dust has the following characteristics among various dust sources.
(1) Centralized fixed-source industrial enterprises have concentrated production processes at their production sites. The discharged dust has the most serious pollution to the atmospheric environment in the neighboring areas. As the distance from the factory area gradually increases, the pollution situation gradually weakens. For example, the impact range of iron and steel enterprises on the atmosphere is basically 10km.
(2) Large smoke and dust emissions Thermal power generation, metallurgy, mining petroleum, chemical and cement enterprises have large production scales and large smoke and dust emissions. Although the scale of light industry production is small, it involves a large number of industries, and the total amount of dust emissions cannot be ignored.
(3) Continuous emissions Most enterprises have uninterrupted production and continuously emit dust into the atmosphere every day.
Particles with a particle size of less than 1 μm in the atmosphere are generated by coagulation, while larger particles come from the pulverization process or the combustion process. The pulverization dry milling method rarely produces particles smaller than a few microns. The combustion process produces several different types of particles, which are produced by:
① Heating can cause substances to evaporate, and these substances then condense into particles of 0.1 to 1 μm;
② The chemical reaction during the combustion process may produce molecular cluster particles smaller than 0.1 μm with a short and unstable lifetime.
③ 1 μm or larger ash or fuel particles will be emitted during mechanical processing;
④ If a liquid fuel spray device is used, extremely fine ash will escape directly;
⑤ Incomplete combustion of fossil fuels will generate soot.
Particulate emissions from gasoline-fueled vehicles contain aerosols of carbon, metallic ash, and hydrocarbons. Metal particles come from the combustion of fuels containing leaded anti-knock agents. Charcoal and unburned hydrocarbons come from incomplete combustion. The particulates emitted by diesel engines mainly contain carbon and hydrocarbon aerosols, which are generated by incomplete combustion under conditions of engine overload.
About 10% to 15% of the total air pollutants are in the form of dust particles. Of the total particulate matter, 3% came from motor vehicles, 5% came from industry, 13% came from power plants, 20% came from industrial boilers, and 9% came from waste disposal. Other particulate matter comes from marine salts, volcanic ash, wind eroded dust, road dust, forest fire products, and plant pollen and seeds.
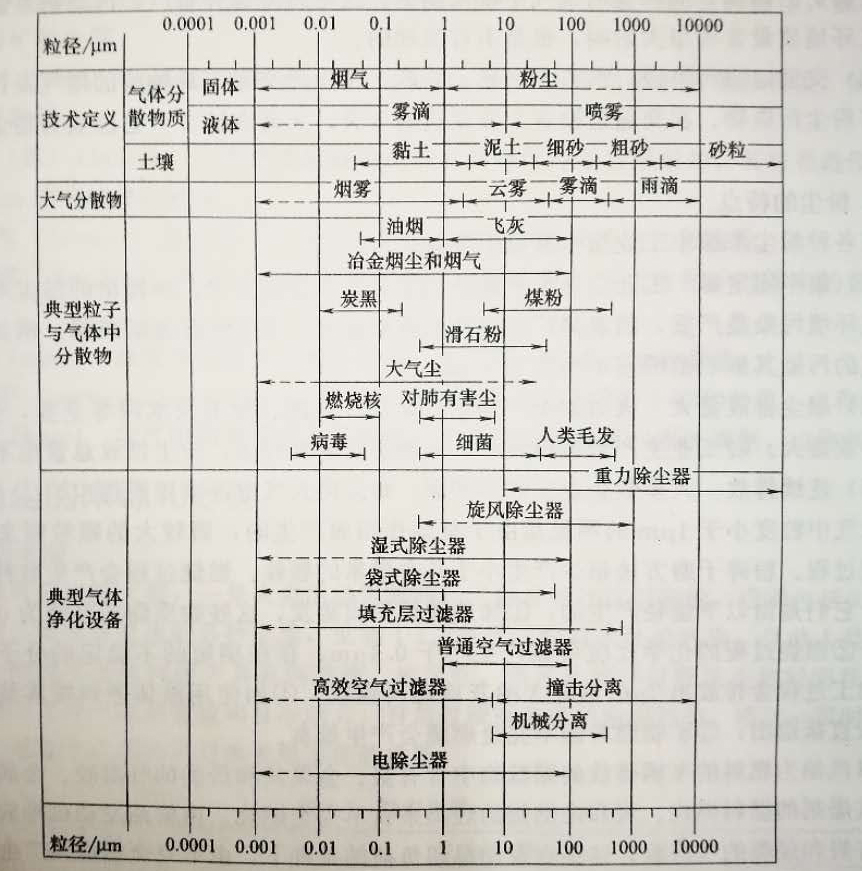
Generally speaking, the particle size of airborne dust particles is 0.00 ~ 500μm, and most of the particle sizes are 0.1 ~ 10m. The movement of dust particles with a particle size smaller than 0.1 μm is similar to that of molecules, and is characterized by a very irregular Brownian motion due to collision with gas molecules. Dust particles with a particle size larger than 1 m, but smaller than 20 μ move with the gas carrying it. Particles larger than 20 m have a clear settling velocity, and therefore, the residence time in the air is very short. The sedimentation speed of dust particles with a density of 1g / cm3 is roughly
These numbers indicate that dust particles are significantly different in the air. The middle part of Figure 1 shows the range of particle sizes for different substances. Any kind of dust removal equipment can remove such particles with particle size distribution. The end section shows the particle size range of particles suitable for capture by different dust removal equipment. Although some types of dust collectors can remove particles within a specified range, in many cases, the dust removal rate changes with the particle size of the particles. For example, the efficiency of a type of dust collector for large particles in a certain range is as high as nearly 10%, but for smaller particles, the efficiency of the dust collector may be close to zero.


